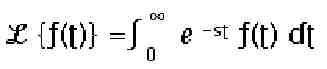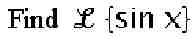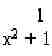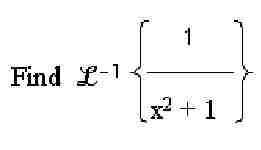Description
The
Laplace transform is a tool in circuitry analysis, methods of design,
and solving differential and integral equations. It is a method for
solving linear constant-coefficient differential equations with
prescribed initial conditions. The Laplace transform is one of the
best-known integral transforms. It is defined by the following:
Usually,
the use of Laplace transforms is effective only if you can also solve
for the inverse problem. This is called the Inverse Laplace transform.
In the instructions below, both the Laplace transform and the Inverse
Laplace transform will be covered.
Calculator symbol key
The procedures in this document use the following text to represent symbol keys:
| Key | Description | Text representation |
|---|---|---|
 | Right shift key. | RS |
 | Left-shift key | LS |
 | Cursor left | cursor-left |
 | Cursor right | cursor-right |
 | Cursor up | cursor-up |
 | Cursor down | cursor-down |

NOTE:
The soft menu keys are the top row of keys. The keys correspond with
the functions displayed in the boxes at the bottom of the display.
Instructions for LAP
Begin by ensuring the flags are set as follows:
- Exact mode must be set (flag -105 clear)
- Numeric mode must not be set (flag -03 clear)
(See User’s Guide, pages 2-20, for more details on flag settings.)
Next, follow the steps listed for the entry mode being used, algebraic or RPN:
Algebraic Entry mode for LAP
If working in Algebraic mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns.,” then press the soft menu OK.
- Cursor-down twice, this will highlight “LAP,” press the soft menu OK.
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression, with respect to the current default variable. The calculator’s default variable is “x”, unless it has been changed.
- Highlight the entire expression in the Equation Writer, then press ENTER.
- This will automatically insert the expression between the parentheses after LAP. Press ENTER.
The calculator will calculate the Laplace transform.
RPN Entry mode for LAP
If working in RPN mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression, with respect to the current default variable. The calculator’s default variable is “x”, unless it has been changed.
- Highlight the entire expression in the Equation Writer then press ENTER.
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns..”, press the soft menu OK.
- Cursor-down twice, this will highlight “LAP,” press the soft menu OK.
The calculator will calculate the Laplace transform.
Example of LAP
Examples are given below for both algebraic and RPN mode for the following problem:
Algebraic Entry mode for LAP example
If working in algebraic mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns.,” then press the soft menu OK.
- 3. Cursor-down twice, this will highlight “LAP,” press the soft menu OK.
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression:
- Press SIN.
- Press X.
- Cursor-right once, this will highlight the expression.
- Press ENTER.
- This will automatically insert the expression between the parentheses after LAP. Press ENTER.
The calculator will perform the Laplace transform.
RPN Entry mode for LAP example
If working in RPN mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression:
- Press SIN.
- Press X.
- Cursor-right once, this will highlight the expression.
- Press ENTER.
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns.,” then press the soft menu OK.
- Cursor-down twice, this will highlight “LAP,” press the soft menu OK.
The calculator will calculate the Laplace transform.
Instructions for ILAP
Begin by ensuring the flags are set as follows:
- Exact mode must be set (flag -105 clear)
- Numeric mode must not be set (flag - 03 clear)
(See User’s Guide, pages 2-20, for more details on flag settings.)
Next, follow the steps listed for the entry mode being used, algebraic or RPN:
Algebraic Entry mode for ILAP
If working in Algebraic mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns..”, press the soft menu OK.
- Cursor-down once, this will highlight “ILAP,” press the soft menu OK.
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression, with respect to the current default variable. The calculator’s default variable is “x”, unless it has been changed.
- Highlight the entire expression in the Equation Writer, then press ENTER.
- This will automatically insert the expression between the parentheses after ILAP. Press ENTER.
The calculator will perform the Inverse Laplace transform.
RPN Entry mode for ILAP
If working in RPN mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression, with respect to the current default variable. The calculator’s default variable is “x”, unless it has been changed.
- Highlight the entire expression in the Equation Writer, then press ENTER.
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns.,” press the soft menu OK.
- Cursor-down once, this will highlight “ILAP,” press the soft menu OK.
The calculator will perform the Inverse Laplace transform.
Example of ILAP
Examples are given below for both algebraic and RPN mode for the following problem:
Algebraic Entry mode for ILAP example
If working in Algebraic mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns.,” press the soft menu OK.
- Cursor-down once, this will highlight “ILAP”, press the soft menu OK.
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression:
- Press 1,then the divide key.
- Press X,yx, 2.
- Cursor-right once, this will highlight x2
- Press +, 1.
- Cursor-right twice, this will highlight the entire expression.
- Press ENTER.
- This will automatically insert the expression between the parentheses after ILAP. Press ENTER.
The calculator will calculate the Inverse Laplace transform.
The answer displayed is as follows:
SIN (X)
RPN Entry mode for ILAP example
If working in RPN mode, follow these steps in the order given:
- Press EQW, this will place you in the Equation Writer.
- Enter the expression:
- Press 1, then the divide key.
- Press X,yx, 2.
- Cursor-right once, this will highlight x2.
- Press +, 1.
- Cursor-right twice, this will highlight the entire expression.
- Press ENTER.
- Press LS, then press CALC.
- Cursor-up once, this will highlight “Differential Eqns.,” press the soft menu OK.
- Cursor-down once, this will highlight “ILAP,” press the soft menu OK.
The calculator will calculate the Inverse Laplace transform.
The answer displayed is as follows:
SIN (X)