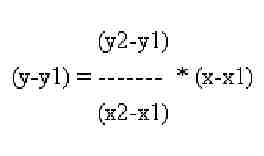Description
With
certain types of problems there are given data sets with values for
several known data points, however the value of a data point that is not
given needs to be determined. To find these unknown data points, make a
guess at what the unknown value should be. One way to make such a guess
is to make a linear estimation based on the closest point on each side
of the value being sought. Such a process is often called interpolation.
The HP 48g and 49g series calculators do not have a function built in
to interpolate an unknown result. This document gives the steps
necessary to enter the equation that can solve for such an interpolation
using the solver.
Example
This example uses a table of logarithms and a problem that interpolates an unknown point from the values given in the table.
Logarithm table
| n | f(n) |
|---|---|
| 15.0 | 2.464973520 |
| 15.1 | 2.471021644 |
| 15.2 | 2.477029845 |
| 15.3 | 2.482998648 |
| 15.4 | 2.488928566 |
Example problem
What is value of f(15.17)?
Solving for the unknown value
To
solve this problem, find a linear estimation between 15.1 and 15.2.
This example will use the point slope form of the equation of a line.
(See Figure 1.)

NOTE: In the example, the x values in the equation would correspond to the n values in the table, while the y values correspond to f(n). Also, variables x1 and y1 refer to one set of data on the table, in this case 15.1, 2.471021664,
while x2 and y2 would refer to the second set of data for n=15.2. The
variables x and y, without subscripts, refer to the data point being
solved for.
Solve for the example problem value of f(15.17) by following these steps:
- Enter the equation solver. Press the RIGHT-SHIFT key, and refer to the following:
- For the HP 48g, press the SOLVE key [7].
- For the HP 49g and 48g II, press the NUMSLV key [7].
- Select option 1 (Solve equation) from the menu.
- Enter the point slope equation into the solver. To do this, make sure that the EQ field is highlighted and then press your single quote keys:
- On the HP 48g, the key is first column, third row.
- On the HP 49g and 48g II, press RIGHT-SHIFT, then ' (the single quote), then the EQW key.
- Type in the following equation: (y-y1)=((y2-y1)/(x2-x1))*(x-x1)
- On the display it will look like this: '(y-y1)=((y2-y1)/(x2-x1))*(x-x1)', being enclosed in the single quotes.
- Then, press ENTER. There should now be six new boxes, one for each variable.
- Enter the values for the two known points, and the value we want to solve for, into the appropriate variables in the solver menu.
- x1 = 15.1
- x2 = 15.2
- y1 = 2.471021644
- y2 = 2.477029845
- x = 15.17
- To solve for the unknown, arrow over to y, and press the soft menu Solve key.
- The answer displayed should be y = 2.4752273847.
To
find another interpolation, for example, f(15.32), go back to Step 2
and repeat the process, entering the new values for x1, x2, y1, y2, and
x.
- x1 = 15.3
- x2 = 15.4
- y1 = 2.482998648
- y2 = 2.488928566
- x = 15.32
Then, solve for y again. The correct answer for this example will be 2.4841846316.
Other related support information
To find
other interpolation methods
search for the word interpolate in the program library at: http://www.hpcalc.org (hosted by BeachNet Communications, which is not affiliated with HP).