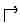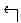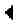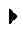Description
The
calculator has two types of memory: RAM and Flash ROM. The following
table gives detailed information on both of these types of memory.
| Type | Amount | Segmented into? | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAM | 512 KB (HP 49g series); 128 KB (HP 48g series) | System memory, user memory, port 0, and port 1 (HP 49g series) | System memory: stores system variables. Users can not access this type of memory.
User Memory: contains the HOME directory (and its subdirectories), history, working memory, and a number of temporary variables created either by the system or by executing programs. User Memory: contains the HOME directory (and its subdirectories), history, working memory, and a number of temporary variables created either by the system or by executing programs. User Memory: contains the HOME directory (and its subdirectories), history, working memory, and a number of temporary variables created either by the system or by executing programs. |
| Flash ROM (HP 49g series) | 2 MB | System memory, and port 2 | System memory: extension of RAM system memory. Port 2: used to store objects that are created or downloaded. |

NOTE:
Objects stored in port memory can be called or executed, but they
cannot be viewed or edited unless they are copied to the main memory.
Calculator symbol key
The procedures in this document use the following text to represent symbol keys:
Using port memory
Objects
that are to be kept should be moved from the user memory to the port
memory. This not only makes more user memory available for everyday
operations, but it puts objects to keep into a safer storage
environment.
Moving objects to port memory
To move objects to the HP 49g series calculator's port memory, do the following:
- Use the FILE MANAGER to select the object to move. To access the FILEMANAGER, press LS, then FILES.
- Press MOVE (the directory tree is redisplayed).
- Press cursor-up and cursor-down until the destination port is highlighted.
- Press OK.
- Press CANCEL to return to the DEFAULT display.
 NOTE: A warning is displayed if an object of the same name already exists in the destination port. In this case, either overwrite the existing object by pressing YES or ALL, cancel the operation by pressing ABORT or NO, or rename the object that is being moved by pressing REN.
NOTE: A warning is displayed if an object of the same name already exists in the destination port. In this case, either overwrite the existing object by pressing YES or ALL, cancel the operation by pressing ABORT or NO, or rename the object that is being moved by pressing REN.